Laboratories

(1)
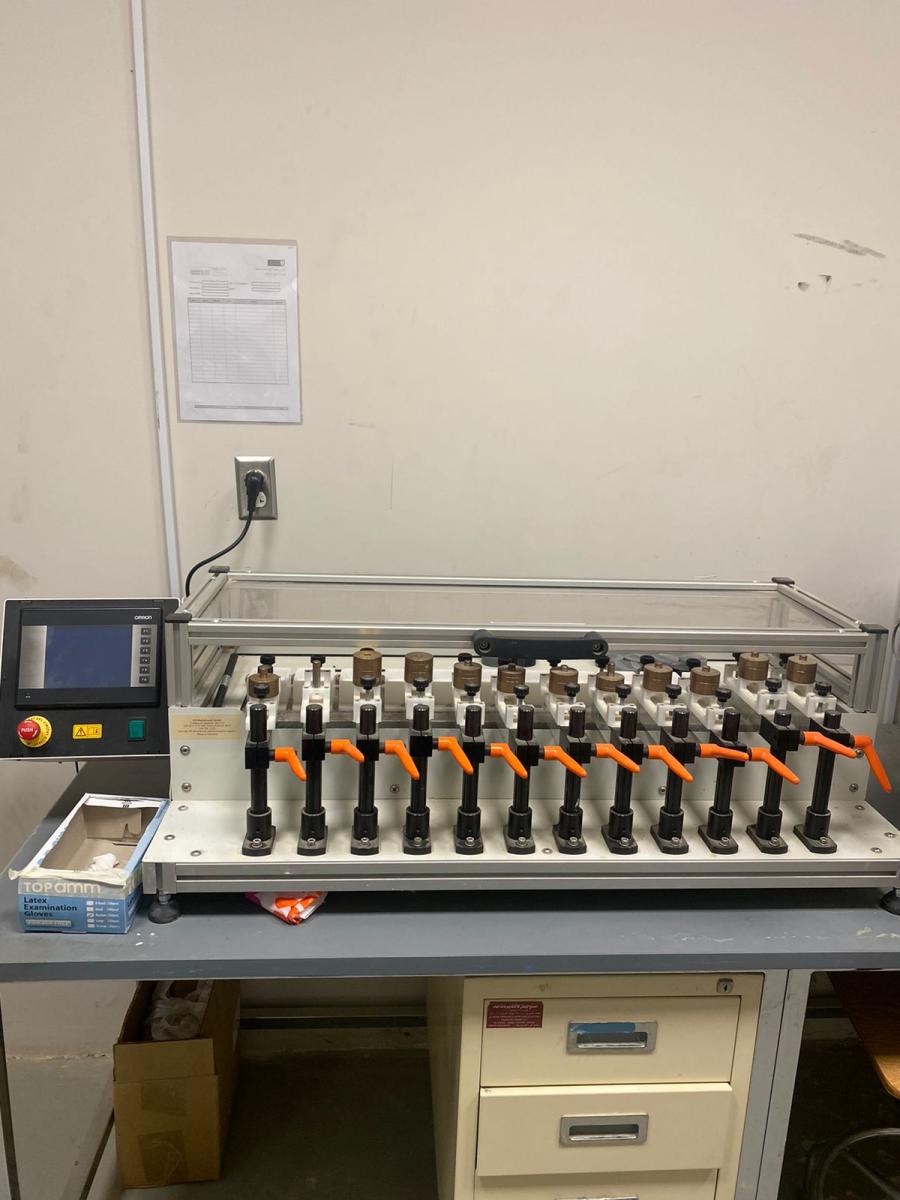
TOOTH BRUSHING SIMULATOR
- The device simulates various brushing movements on the surfaces of tested material.
- The individual specimens may be of various forms and materials (hardness), and may be loaded with various levels of contact pressure.
- The specimen chambers are separated from each other so that each specimen can be operated with its own liquid (e.g. toothpaste-water mix).
- A high-grade motion controller guarantees exact speeds and trajectories which can be adjusted with a very high degree of precision.

(2)
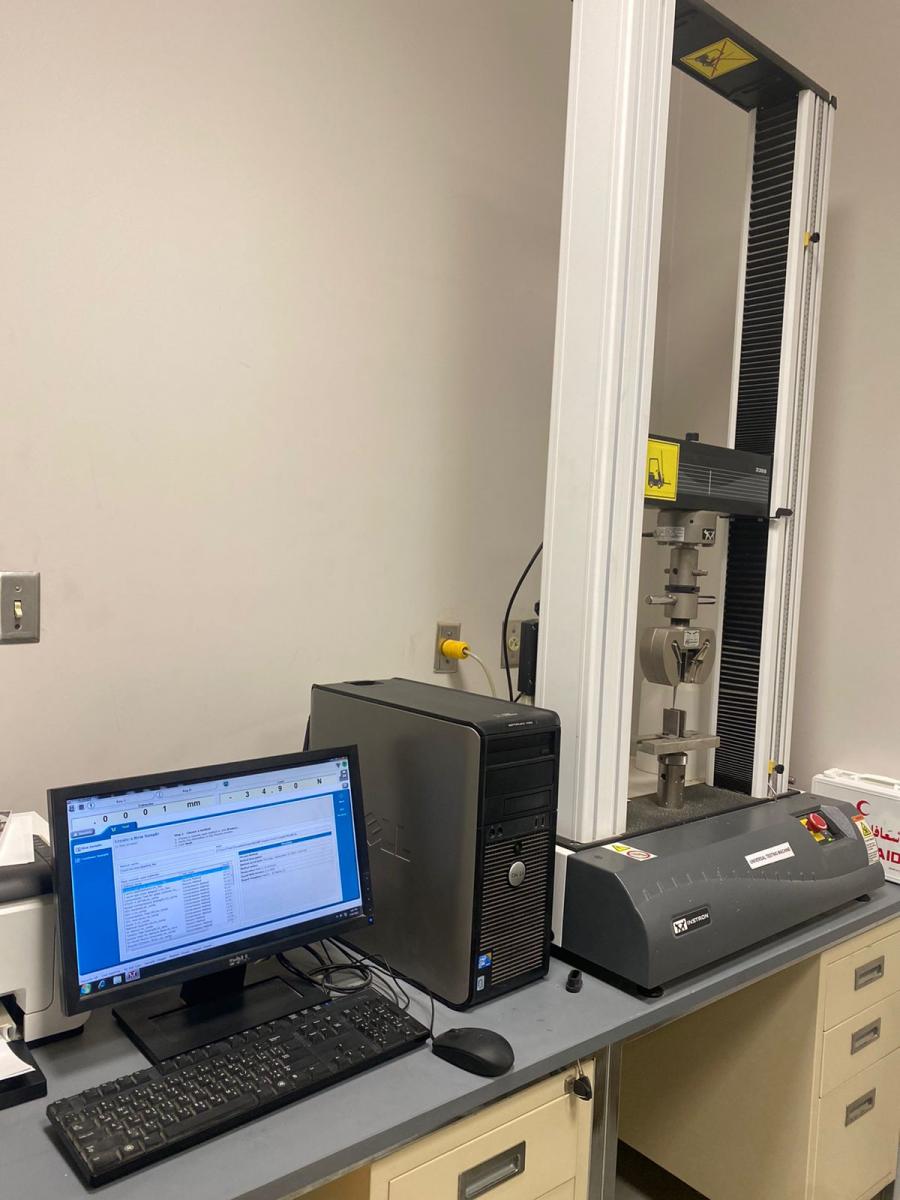
UNIVERSAL TESTING MACHINE
- A universal testing machine is used to assess the strength of materials
- This device is used to test specimen for tensile strength, compressive strength, shear strength, other important laboratory test
- This device measures the mechanical properties in static conditions.

(3)
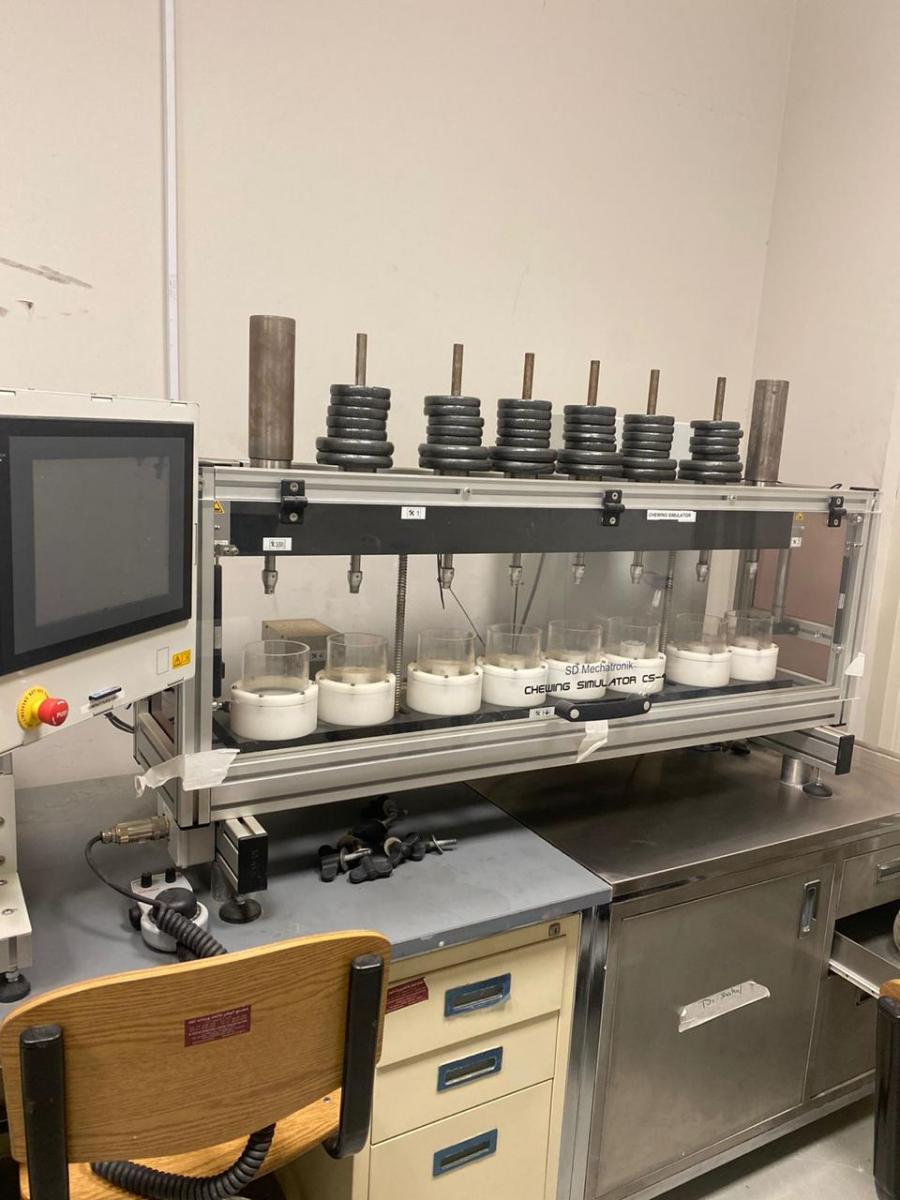
CHEWING SIMULATOR
- A chewing simulator is a device that simulates the chewing process for dental samples.
- This device is used for fatigue testing, and to measure resistance to fracture and wear of a material.
- The individual specimens may be of various forms and materials (hardness), and may be loaded with various levels of contact pressure.
- The specimen chambers are separated from each other so that each specimen can be operated with its own liquid
- A high-grade motion controller guarantees exact speeds and trajectories which can be adjusted with a very high degree of precision.

(4)
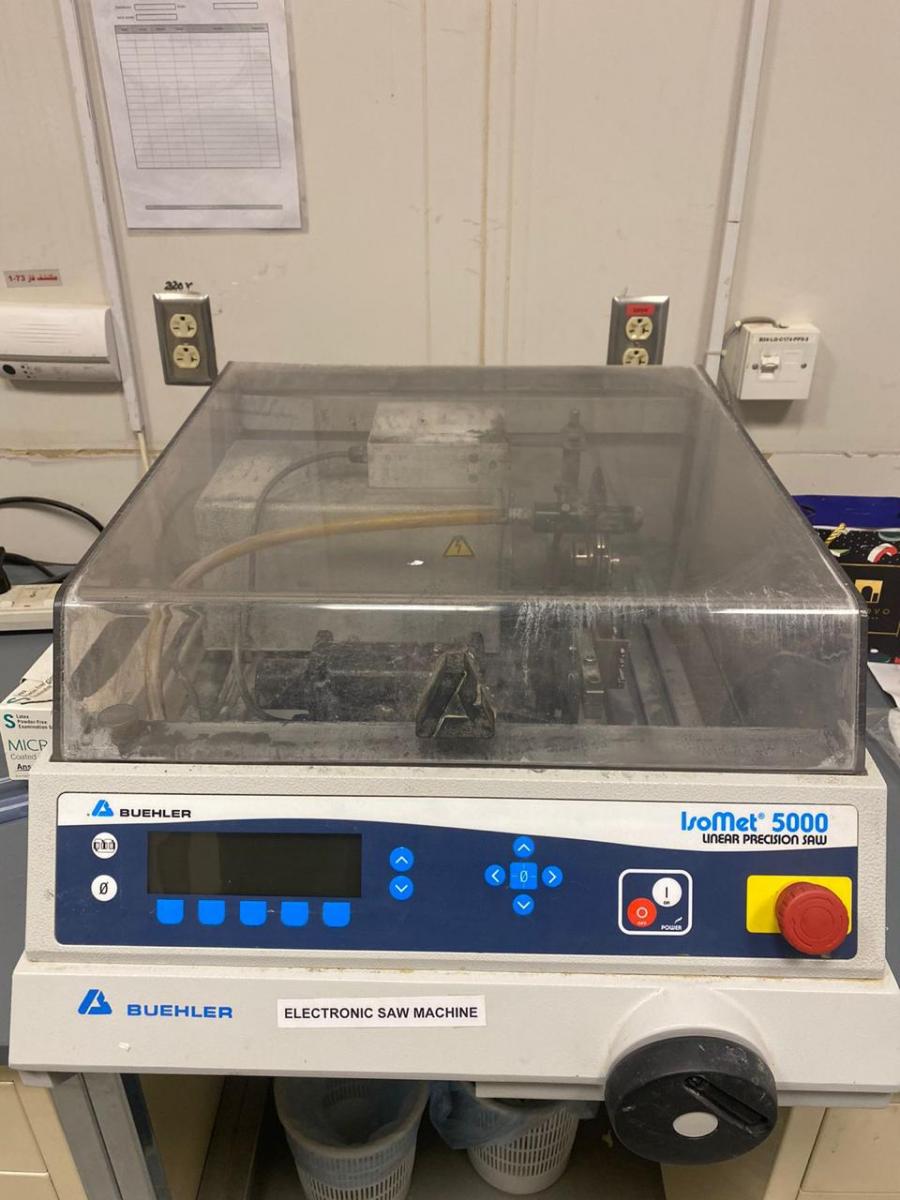
ELECTRIC SAW DEVICE
- This device is used for sample preparation in varying dimensions
- It is used for precision cutting of the samples
- The device is equipped with water coolant for cooling down the samples during cutting
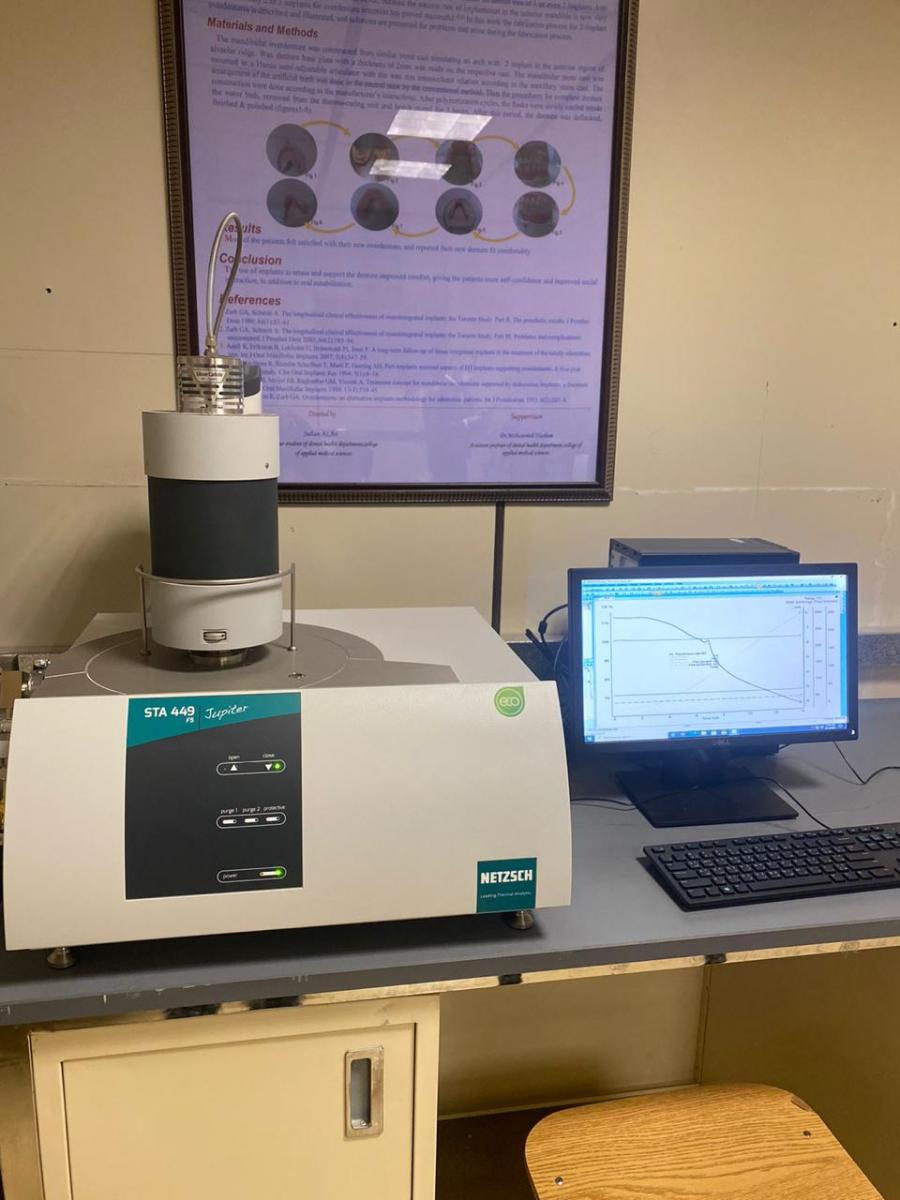

(5)
THERMAL ANALYZER
- This device is used to determine simultaneous changes of mass (TG) and caloric reactions (DSC) of a sample in the temperature range from 0°C up to 1600°C.
- It measures heat flow and weight changes in sample material at varying temperarure.
- The device measures how much a sample absorbs or releases energy during heating or cooling.

(6)
NANOMECHANICAL TESTER
- Provide precise, reliable and repeatable measurements of hardness, Young’s modulus, and other mechanical properties of the materials.
- It provides mechanical properties of a material at nano level
- It can generate the graph between applied load and deformation

(7)
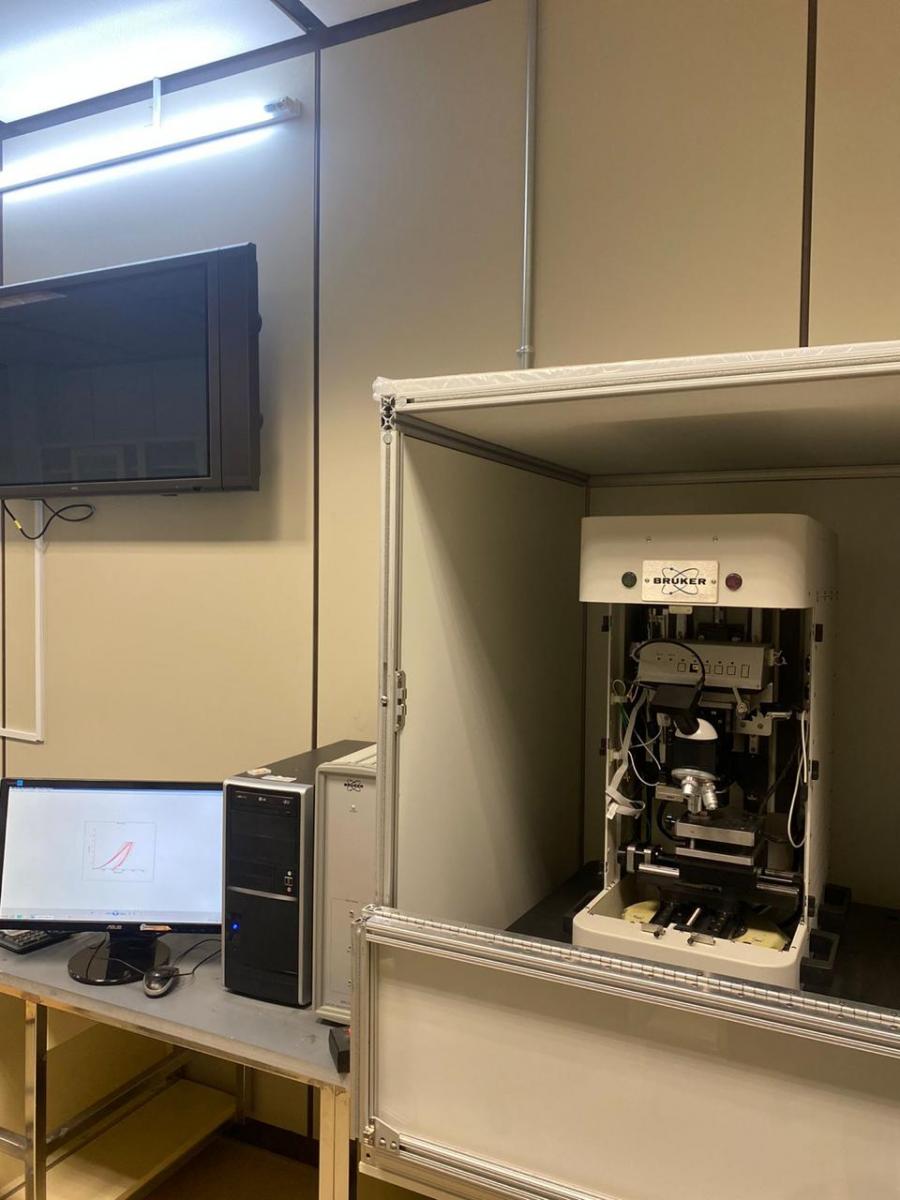
RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY
- Raman Spectroscopy is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique which provides detailed information about chemical structure, phase and polymorphy, crystallinity and molecular interactions
- It is based upon the interaction of light with the chemical bonds within a material.
- Typically, a Raman spectrum is a distinct chemical fingerprint for a particular molecule or material, and can be used to very quickly identify the material, or distinguish it from others
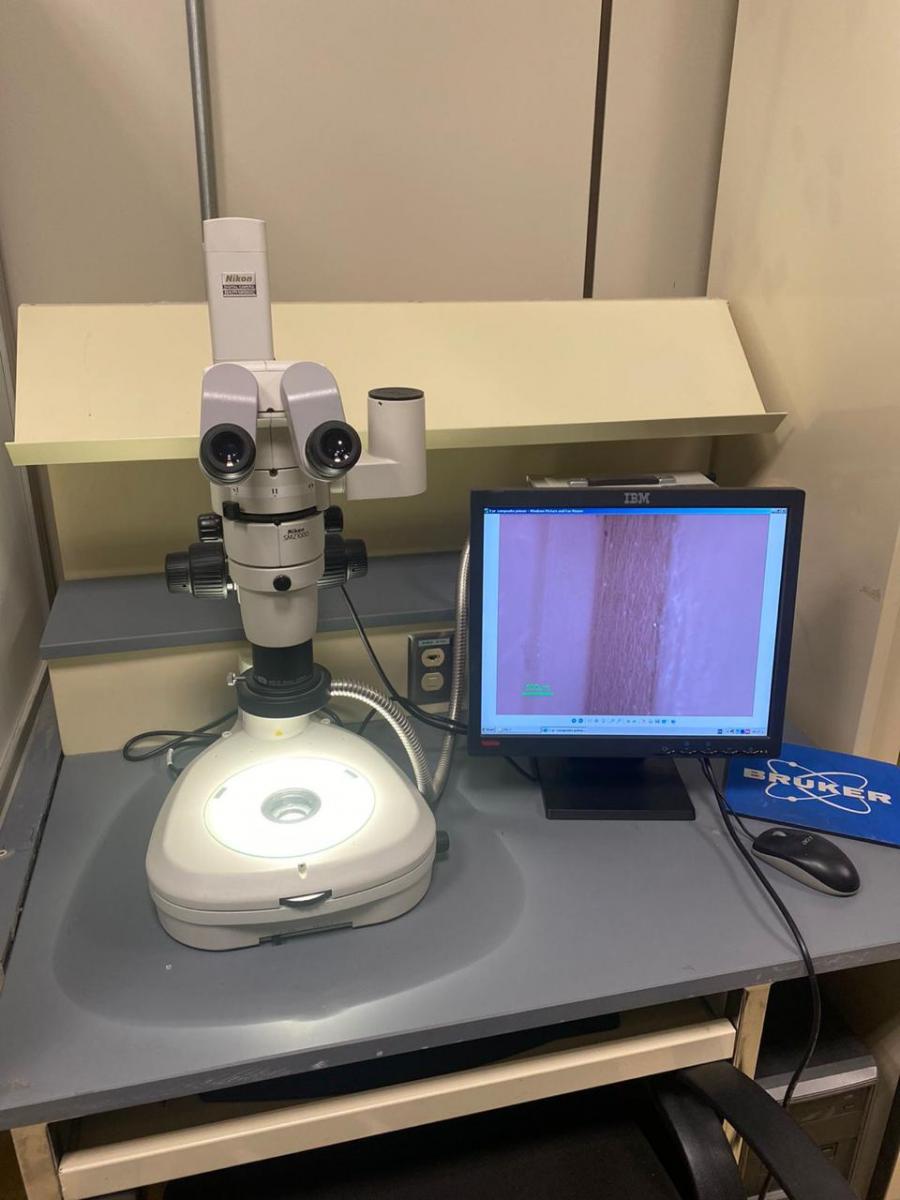
(8)
STEREOMICROSCOPE
- The device is used for visualization of the samples.
- The attached lens can magnify the sample upto 25X.
- The images can be generated using a software.

(9)
TENSIOMETER
- Provides useful information about the wetting characteristics of a surface and a liquid.
- By using different probe liquids with known polar, non-polar, hydrogen-bond energy components, the surface free energy of a solid surface can be determined through contact angle measurement.
- The hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of a material can be measured with this device.

(10)
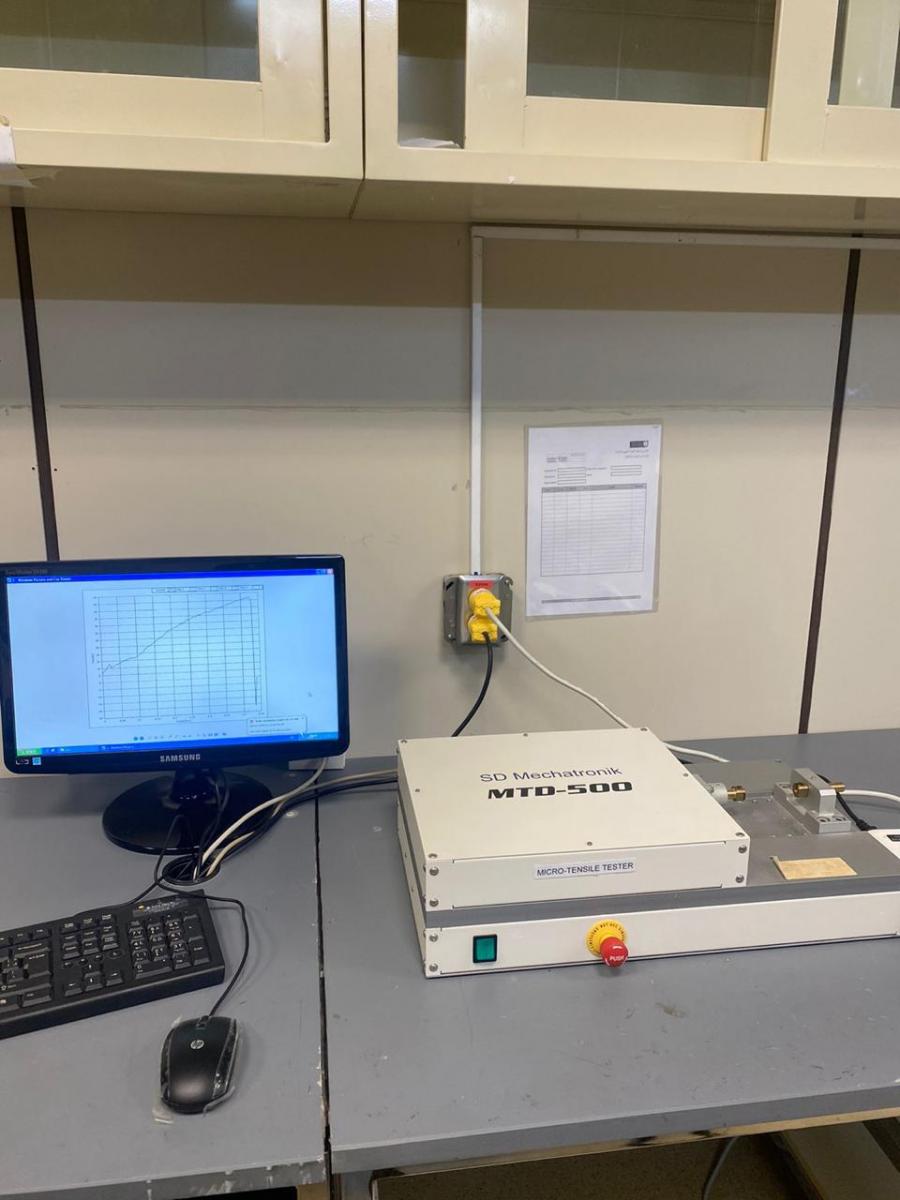
MICROTENSILE TESTER
- The tensile property of a material at micro level can be measured
- Micro-tensile testing can be used to quantify the mechanical properties of individual interfaces or phases within a material
- In addition, measurements on the microscale can be used to detect and investigate single plastic deformation mechanisms.
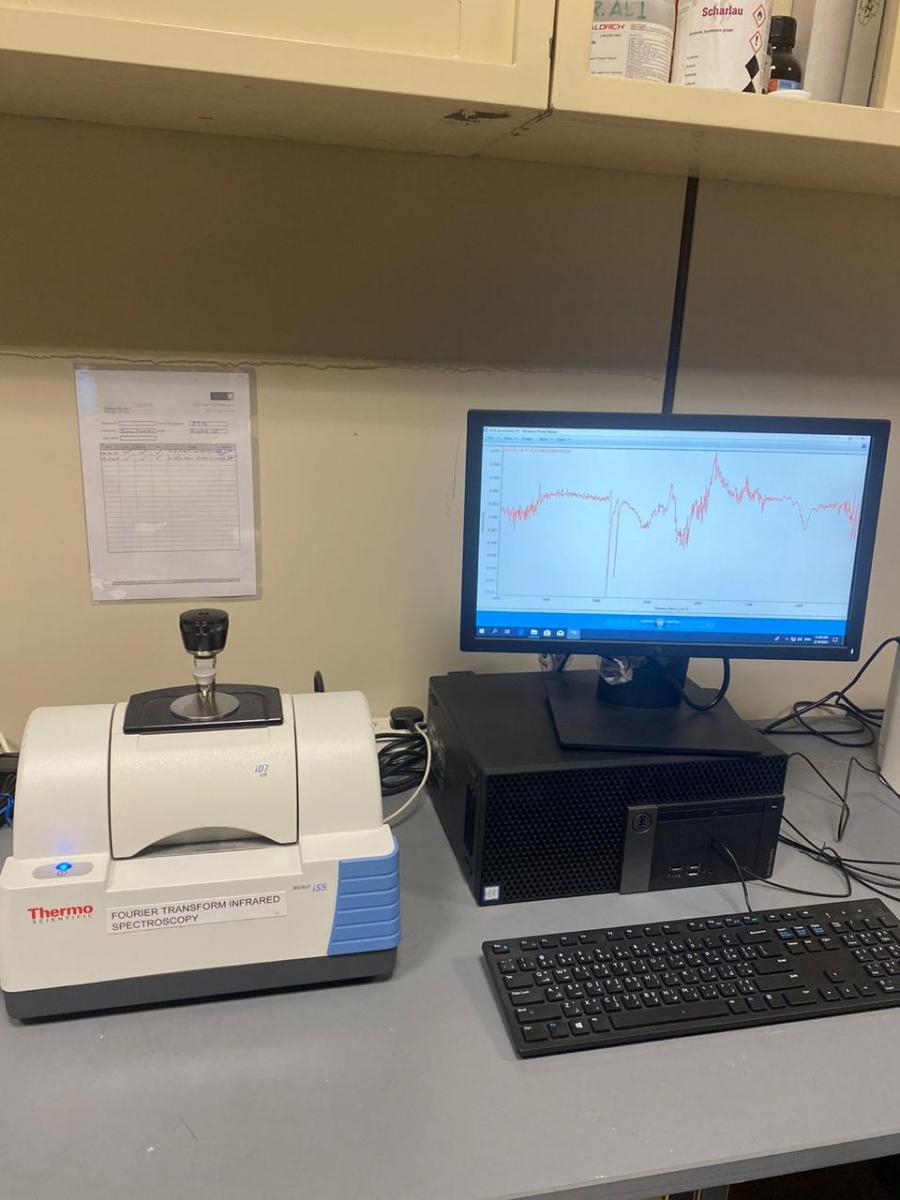

(11)
FTIR
- FTIR spectroscopy is used to quickly and definitively identify compounds such as compounded plastics, blends, fillers, paints, rubbers, coatings, resins, and adhesives.
- FTIR spectra reveal the composition of solids, liquids, and gases.
- The formation of a new chemical compound can be detected using this device
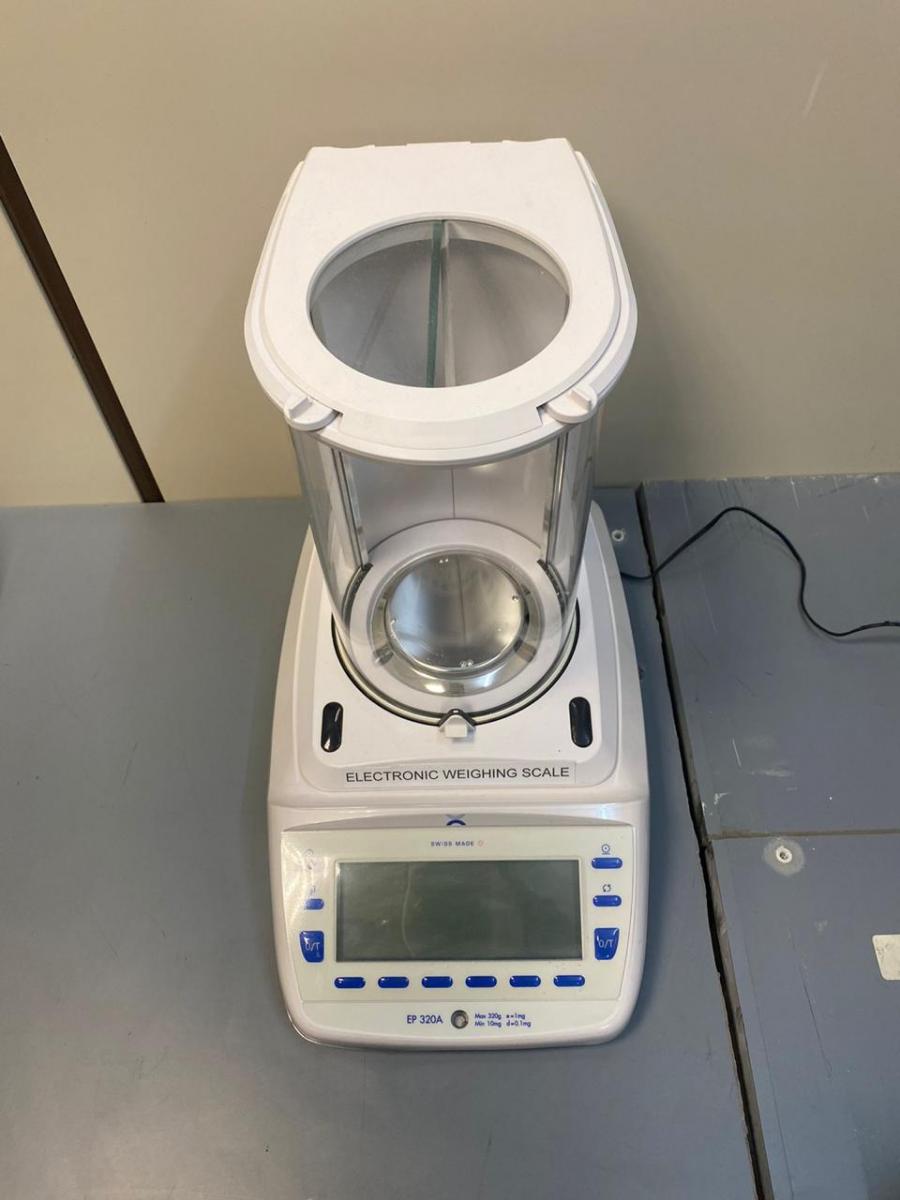

(12)
ELECTRONIC WEIGHING SCALE
- The device is used to measure the mass/weight of a substance precisely in enclosed chamber.
- The device can measure the weight as low as 0.00001 gram
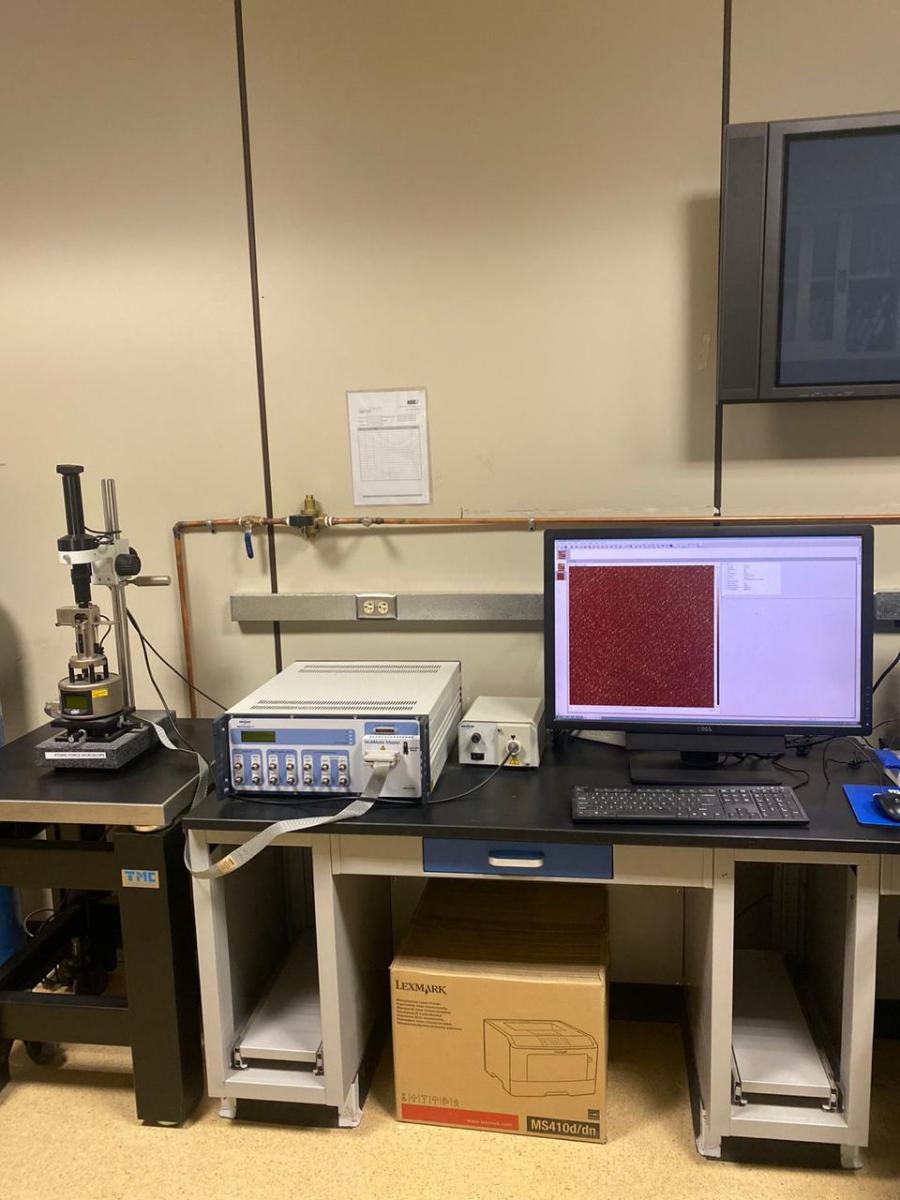

(13)
ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPE
- This instrument has become the most widely used tool for imaging, measuring and manipulating matter at the nanoscale
- The primary role of this device is measuring surface topography.
- It can be used to quantify the roughness of surfaces at nano level
- It can generate 3D images
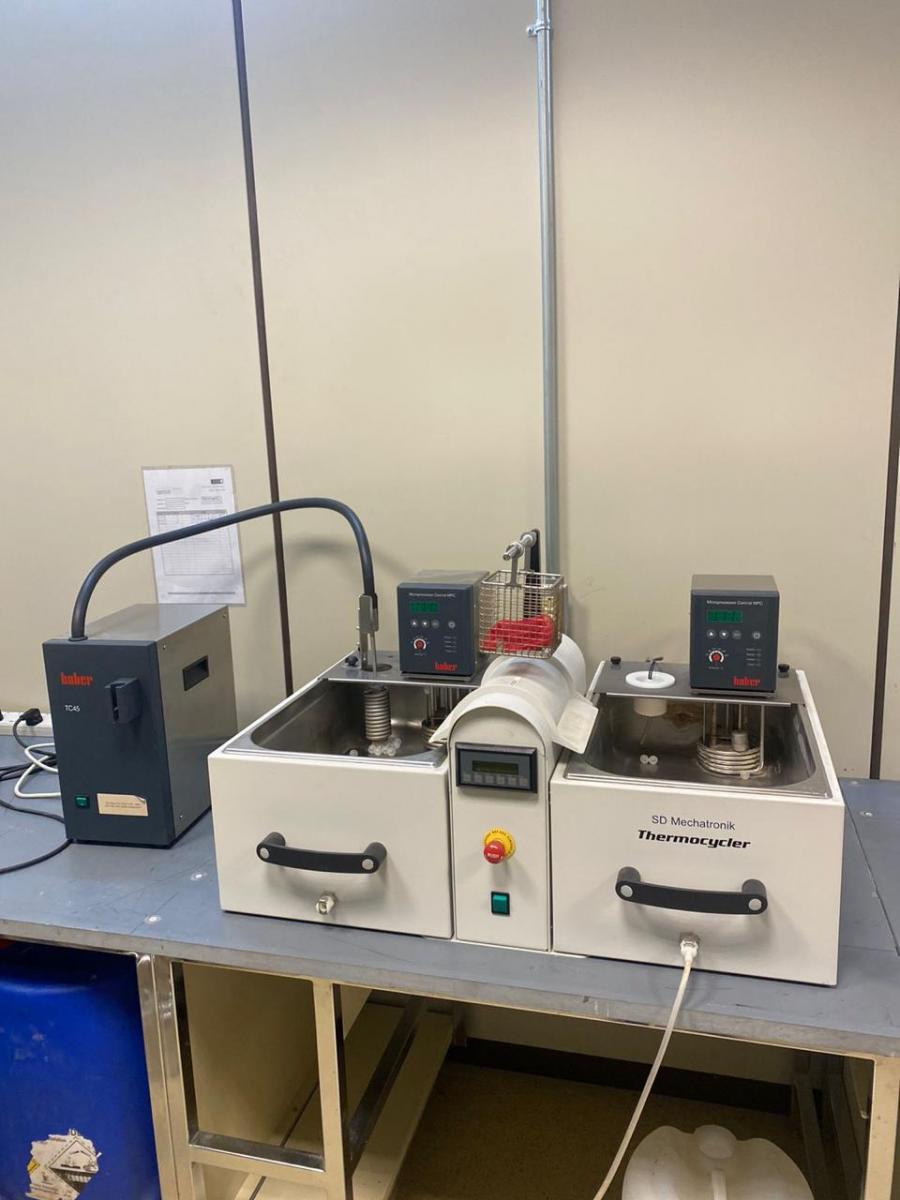

(14)
THERMO CYCLER
- The device is mainly used to age a material to simulate the clinical condition
- The device is used for quick ageing of a material prior to testing of a material.
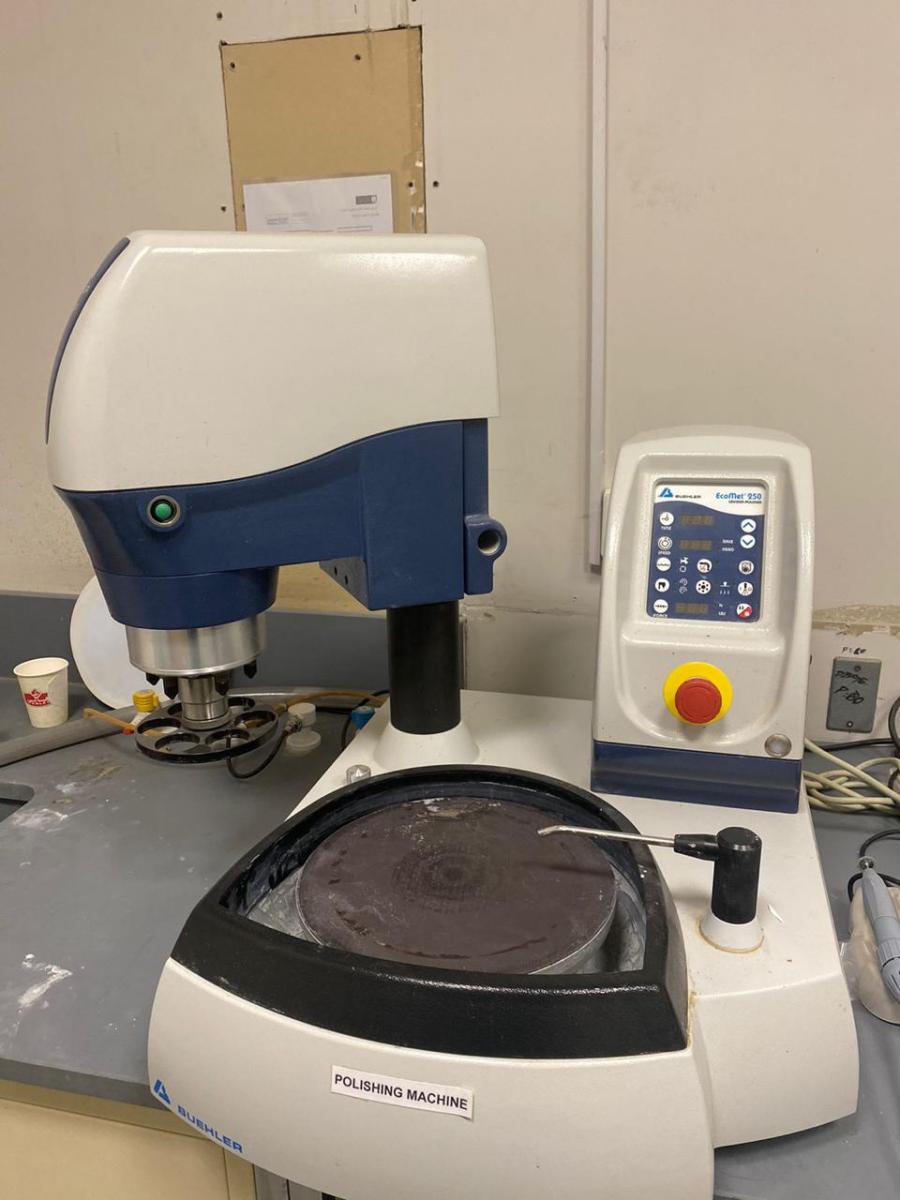

(15)
POLISHING DEVICE
- This device is used for sample preparation and finishing.
- The device polish the surface of specimen without wearing it out excessively.
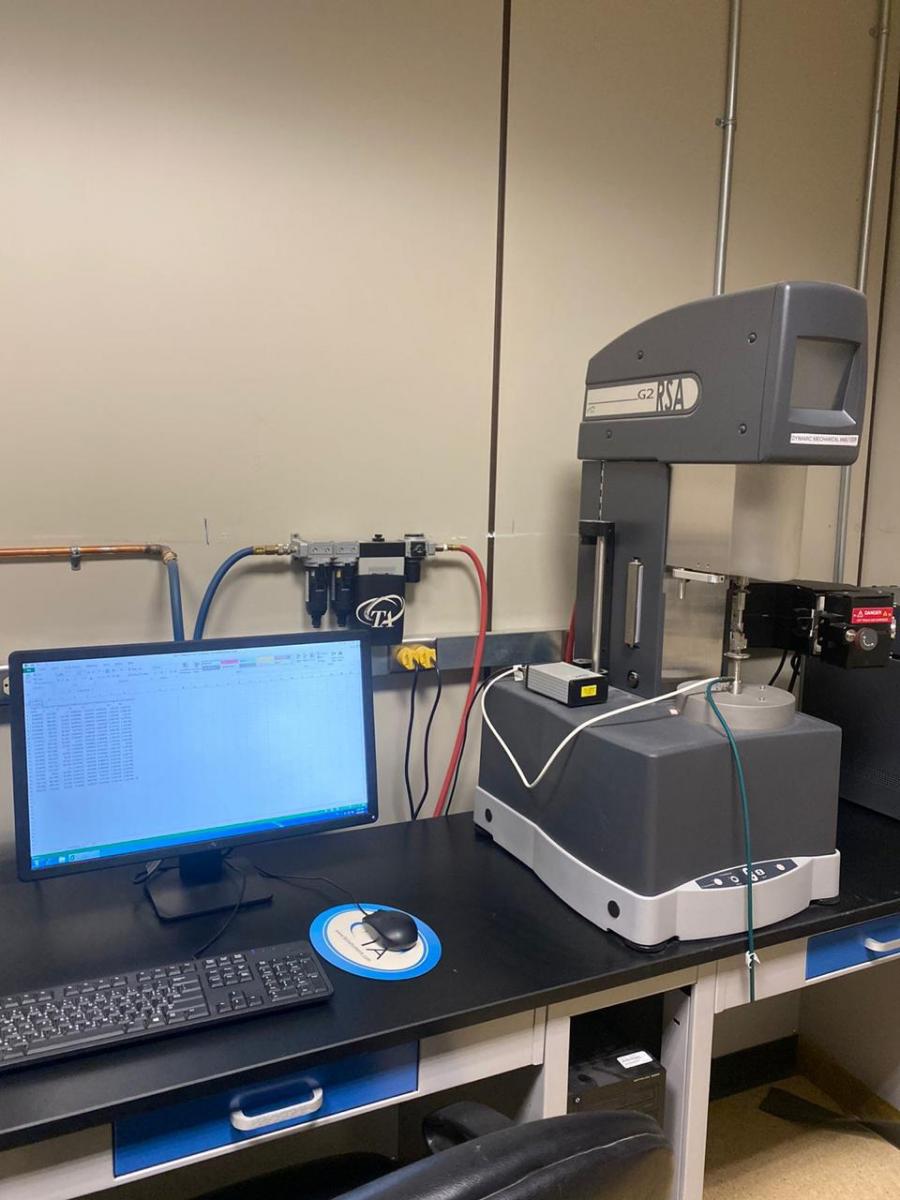

(16)
DYNAMIC MECHANICAL ANALYZER
- Dynamic mechanical analysis is a powerful and commonly used tool to study the viscoelastic behavior of polymers
- It involves measuring a material's response to an oscillating stress.
- The device can measure thermal transitions in polymers, including the glass transition temperature.
